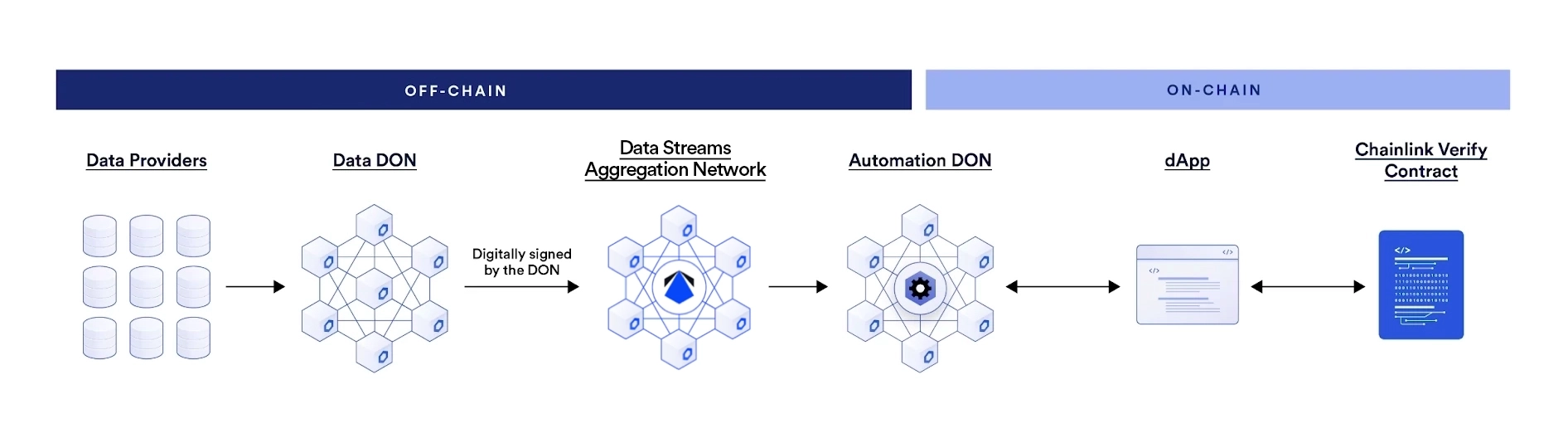
Data Streams Architecture
High Level Architecture
Chainlink Data Streams has the following core components:
- A Chainlink Decentralized Oracle Network (DON): This DON operates similarly to the DONs that power Chainlink Data Feeds, but the key difference is that it signs and delivers reports to the Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network rather than delivering answers onchain directly. This allows the Data Streams DON to deliver reports more frequently for time-sensitive applications. Nodes in the DON retrieve data from many different data providers, reach a concensus about the median price of an asset, sign a report including that data, and deliver the report to the Data Streams Aggregation Network.
- The Chainlink Data Streams Aggregation Network: The Data Streams Aggregation Network stores the signed reports and makes them available for retrieval. It can deliver these reports to Chainlink Automation upon request (Streams Trade) or provide direct access via the API (Streams Direct).
- The Chainlink Verifier Contract: This contract verifies the signature from the DON to cryptographically guarantee that the report has not been altered from the time that the DON reached concensus to the point where you use the data in your application.
Streams Trade Architecture
Using Chainlink Automation with Data Streams automates trade execution and mitigates frontrunning by executing the transaction before the data is recorded onchain. Chainlink Automation requests data from the Data Streams Aggregation Network. It executes transactions only in response to the data and the verified report, so the transaction is executed correctly and independently from the decentralized application itself.
Example trading flow using Streams Trade
One example of how to use Data Streams with Automation is in a decentralized exchange. An example flow might work using the following process:
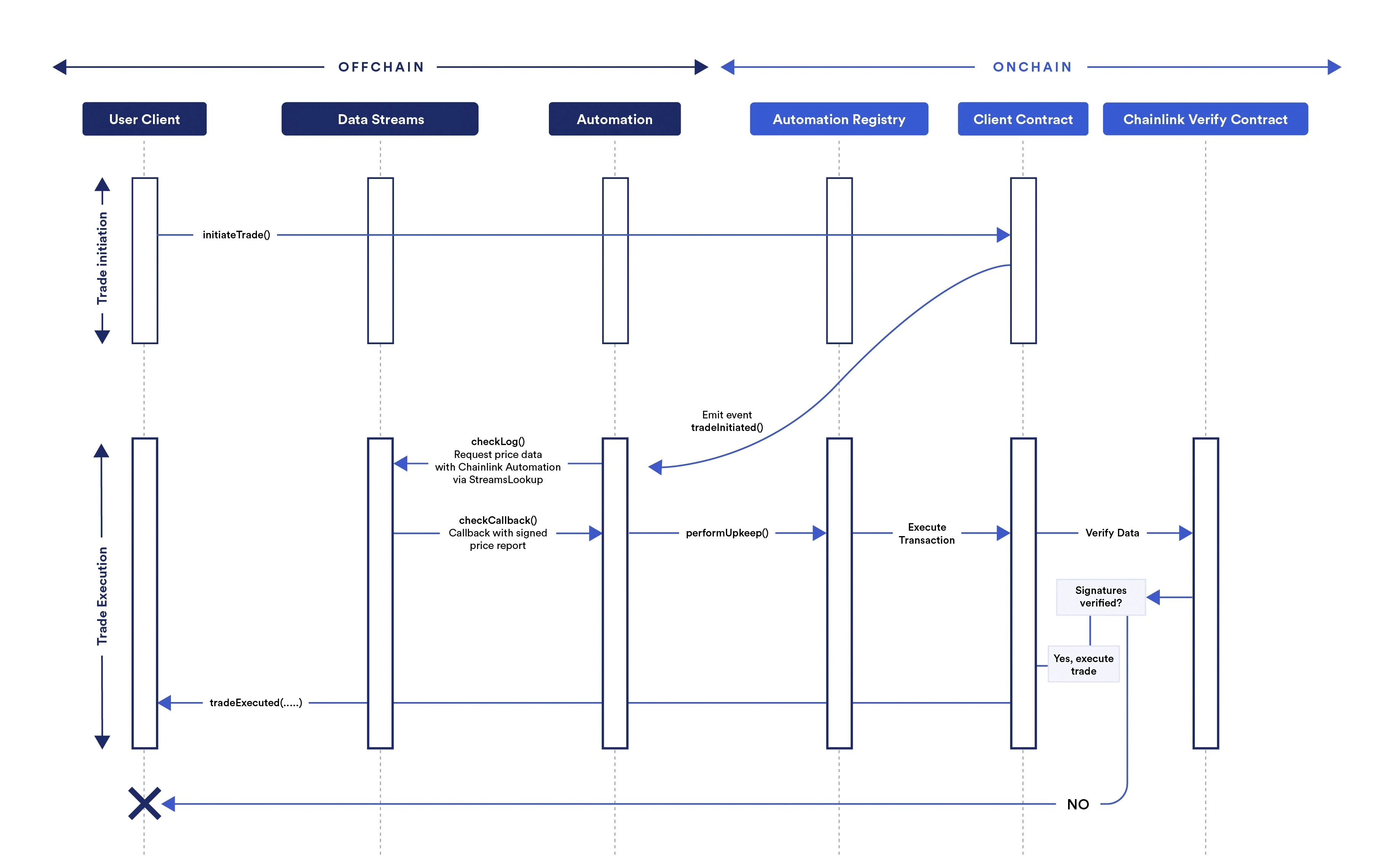
- A user initiates a trade by confirming an
initiateTradetransaction in their wallet. - The onchain contract for the decentralized exchange responds by emitting a log trigger event.
- The Automation upkeep monitors the contract for the event. When Automation detects the event, it runs the
checkLogfunction specified in the upkeep contract. The upkeep is defined by the decentralized exchange. - The
checkLogfunction uses arevertwith a custom error calledStreamsLookup. This approach aligns with EIP-3668 and conveys the required information through the data in therevertcustom error. - Automation monitors the
StreamsLookupcustom error that triggers Data Streams to process the offchain data request. Data Streams then returns the requested signed report in thecheckCallbackfunction for Automation. - Automation passes the report to the Automation Registry, which executes the
performUpkeepfunction defined by the decentralized exchange. The report is included as a variable in theperformUpkeepfunction. - The
performUpkeepfunction calls theverifyfunction on the Data Streams onchain verifier contract and passes the report as a variable. - The verifier contract returns a
verifierResponsebytes value to the upkeep. - If the response indicates that the report is valid, the upkeep executes the user's requested trade. If the response is invalid, the upkeep rejects the trade and notifies the user.
This is one example of how you can combine Data Streams and Automation, but the systems are highly configurable. You can write your own log triggers or custom logic triggers to initiate Automation upkeeps for a various array of events. You can configure the StreamsLookup to retrieve multiple reports. You can configure the performUpkeep function to perform a wide variety of actions using the report.
Read the Getting Started guide to learn how to build your own smart contract that retrieves reports from Data Streams using the Streams Trade implementation.
Streams Direct Architecture
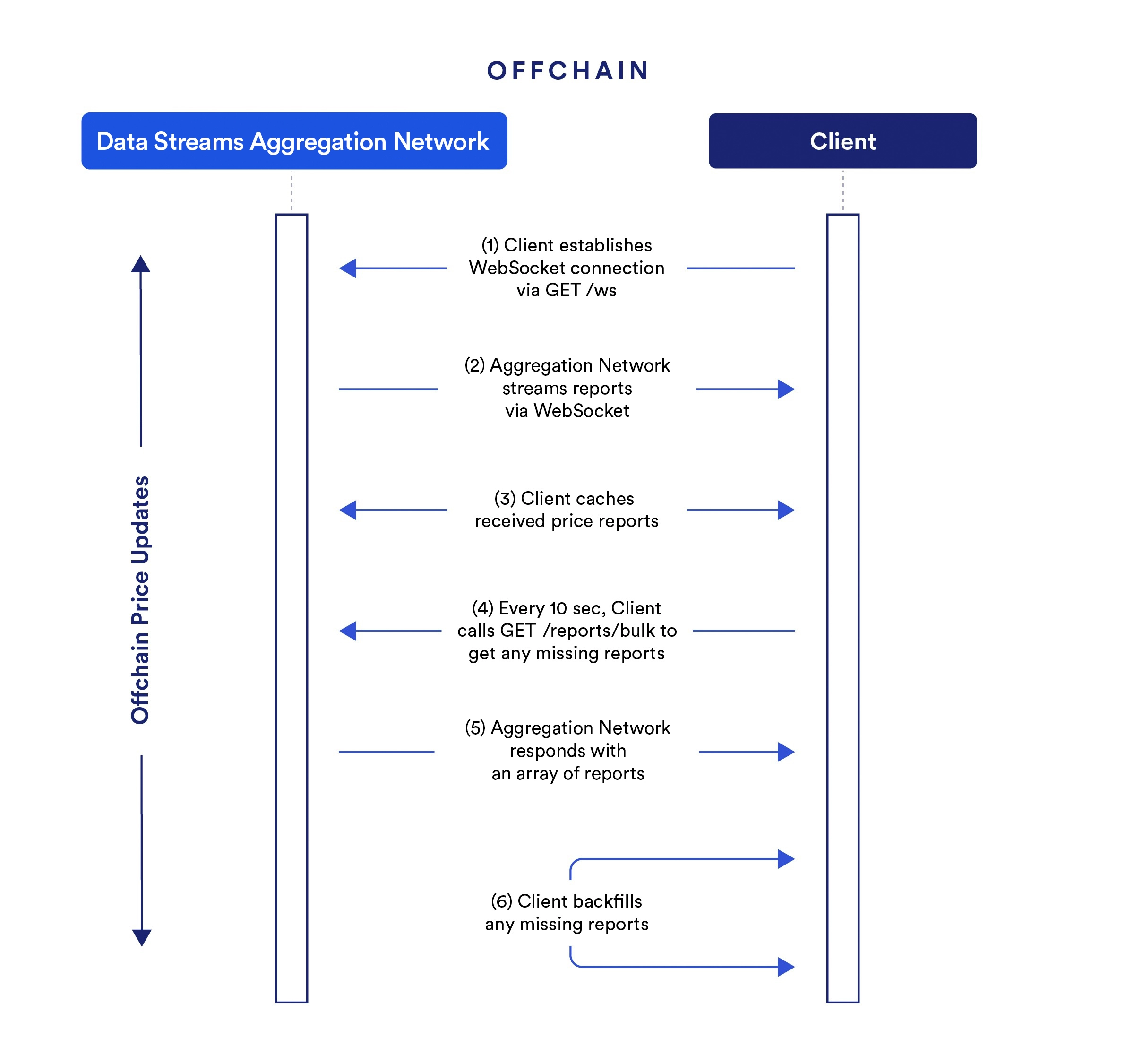
Example of offchain price updates with Streams Direct
Streams Direct enables seamless offchain price updates through a mechanism designed for real-time data delivery. Here is an example of how your Client will benefit from low-latency market data directly from the Data Streams Aggregation Network.
-
The Client opens a WebSocket connection to the Data Streams Aggregation Network to subscribe to new reports with low latency.
-
The Data Streams Aggregation Network sends price reports via WebSocket, which gives the Client instant access to updated market data.
-
The Client stores the price reports in a cache for quick access and use, which preserves data integrity over time.
-
The Client regularly queries
/client/bulkfor any missed reports to ensure data completeness. -
If the Data Streams Aggregation Network identifies missed reports, it sends back an array of these reports. This mechanism allows the Client to update its cache and to keep the data set complete and up-to-date.